Okay, when we are nearly through with all things fiber splice diagrams and splicing matrixes, and now anyone can easily design splice sheets in several clicks using splice.me, let’s discuss what happens when you grab a spool of optic cable and want to hook it on a pole. I mean, you have done fiber network design, you’ve got all necessary technical drawings, a fiber map, budget loss calculation, etc. Go and attach the cable? No. First perform pole loading analysis, because your fiber cable adds loading to a pole, and show it to your local public utility company.
Table of contents
What is utility pole loading analysis?
Why is it important?
How is utility pole loading analysis usually carried out?
Pole loading reports
Applicable regulations
What to start from?
Considerations in pole loading analysis
What you get
Is O-calc the best software for pole loading analysis?
FAQ
What is utility pole loading analysis?
Pole loading analysis, or simply PLA, involves calculating and evaluating the forces acting on a utility pole, such as:
- Dead loads – the weight of the pole, crossarms, transformers, wires, cables, and attached equipment.
- Live loads – temporary forces like wind and ice affecting wires and cables according to a chosen load case.
- Safety factors – reserve strength to handle expected conditions or degradation over time.
The goal is to ensure that the pole and its components can safely withstand expected forces without failure, buckling, or undue stress.
Why is it important?
Frankly speaking, you just don’t want the pole to fail and fall on your head.
- Safety – prevents pole failures that could harm people, disrupt services, or damage property.
- Compliance – ensures adherence to engineering standards and legal regulations, like NESC. Ensures you meet the cable sag limitations.
- Longevity – extends the lifespan of poles by preventing premature failure.
- Efficiency – helps in optimal material use, saving costs and resources.
- Resilience – ensures poles can withstand severe weather.
How is utility pole loading analysis usually carried out?
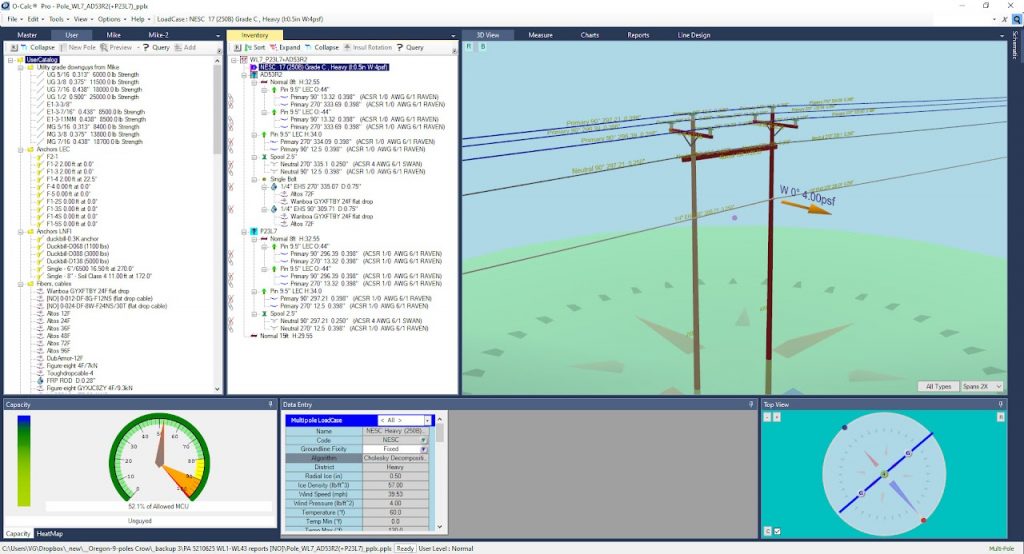
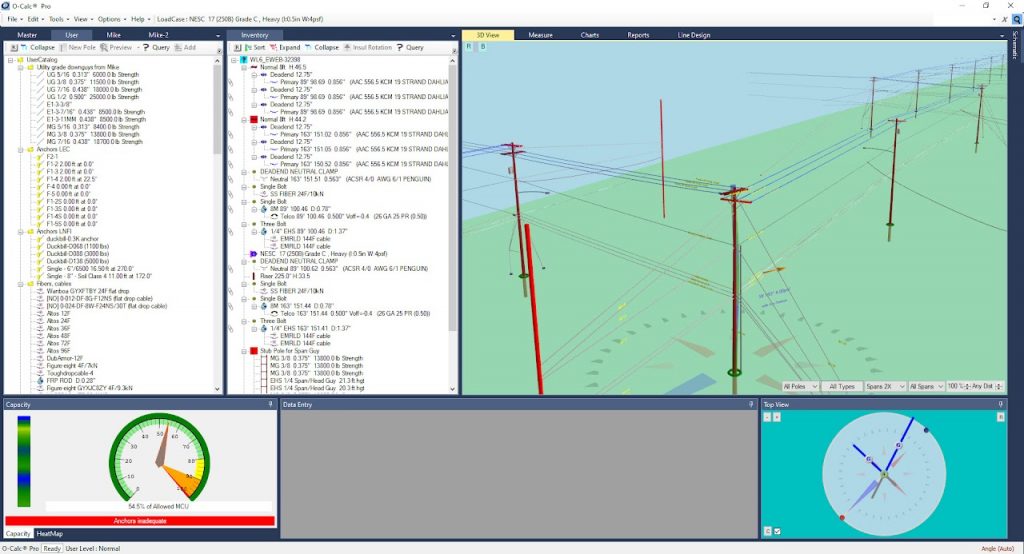
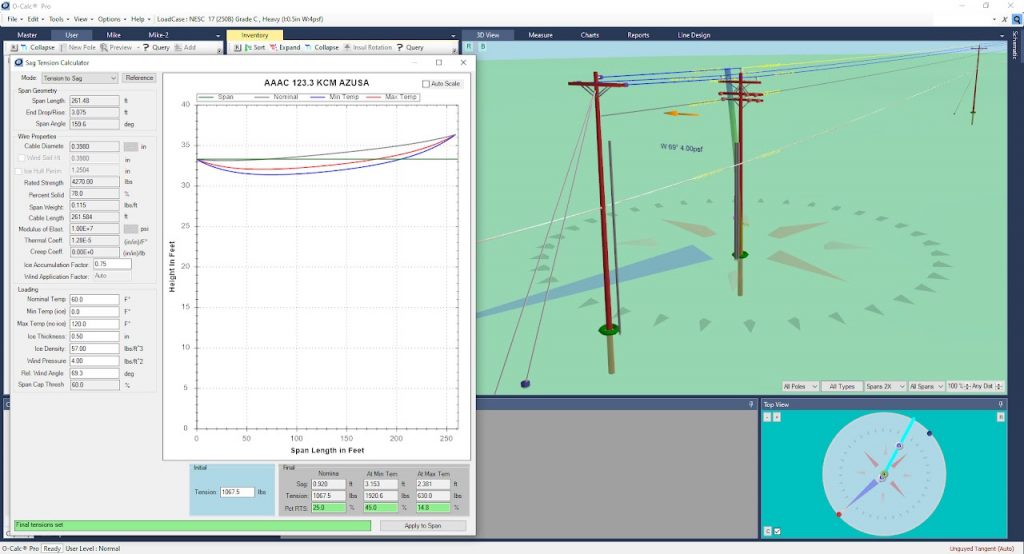
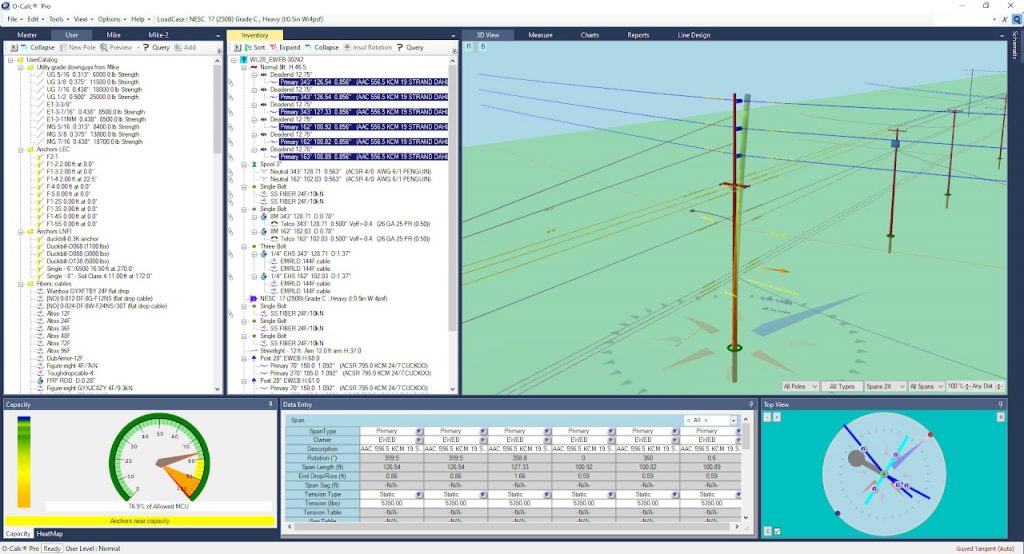
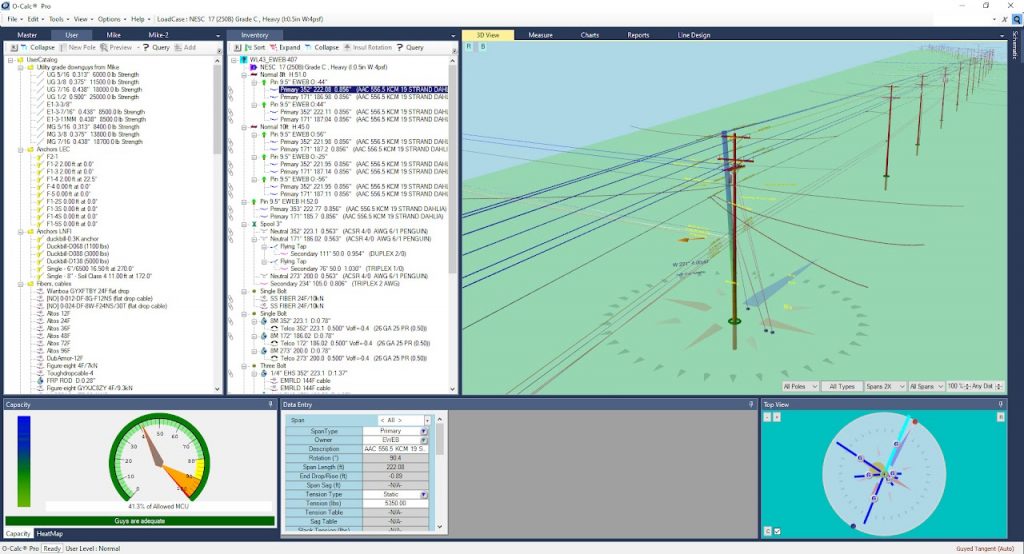
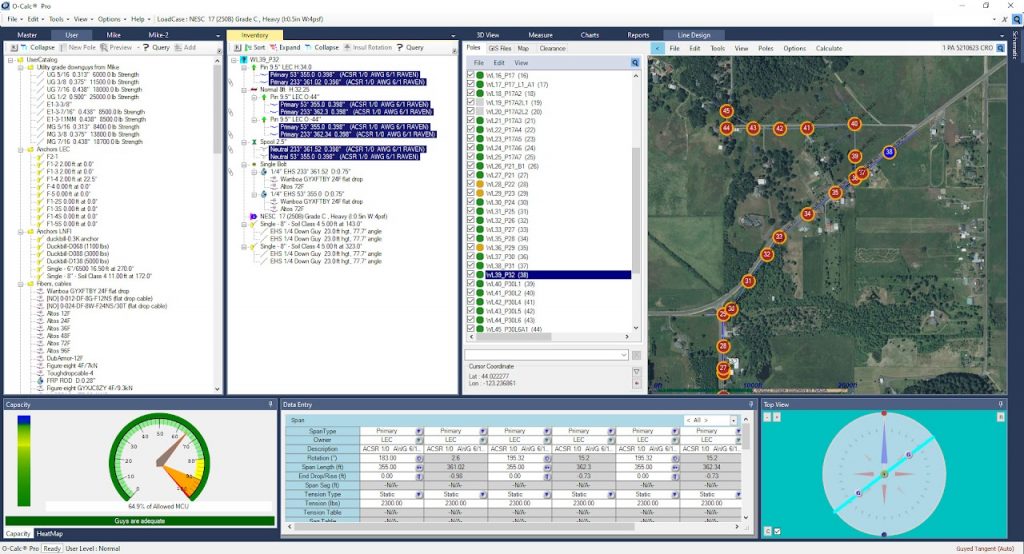
O-Calc Pro allows designing any types of wooden poles, up to 75 ft tall, all kinds of paired and connected poles. Transmission, subtransmission lines, secondary subscriber lines, all types of communication cables can be designed and carefully analyzed, under any given climatic conditions and in different construction zones. O-Calc has lots of equipment and guying solutions at hand, any user cable or equipment can be custom designed as well.
Pole loading reports
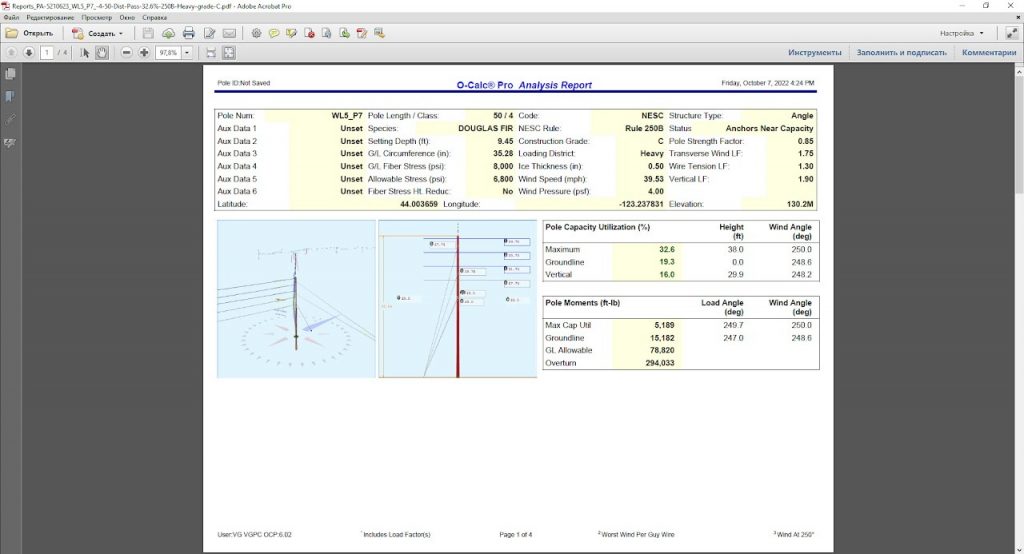
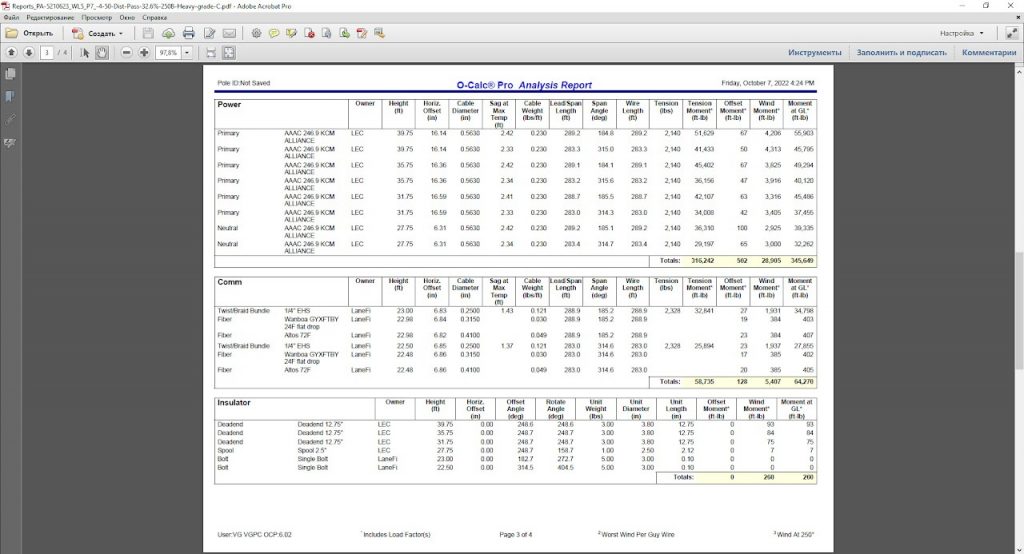
The final result of pole loading analysis is the report file for each and every pole, which shows lateral and vertical pole loading in % compared to maximum allowable loading. Pole loading is assumed as PASSED if the loading is within 85% of allowable (in most cases) according to Table 261-1 of NESC 2017.
Reports are handy in reviewing correctness of such things as anchor placement, downguys tension, braces load, conductor and communication cables tension, etc. Reports show load share between attachers.
Applicable regulations
- National Electric Safety Code (NESC) – specifies requirements for pole loading, clearances, and safety factors.
- ANSI O5.1 – covers wood pole specifications for strength and quality.
- Local and regional codes – additional guidelines based on geographical or jurisdictional considerations.
In other countries, equivalent standards like the IEC or local utility codes may apply.
What to start from?
An initial survey is neccessary to gather all possible field data concerning poles one needs to attach to. It can be made and presented in different ways, but at least it should bear the names of poles, their height and class. Height of attachment of existing conductors and cables should be collected, as well as existing anchor types and their lead lengths. The type of existing conductors should be requested from your utility company. Field photos should be provided. The appearance of the collected field data does not really matter:
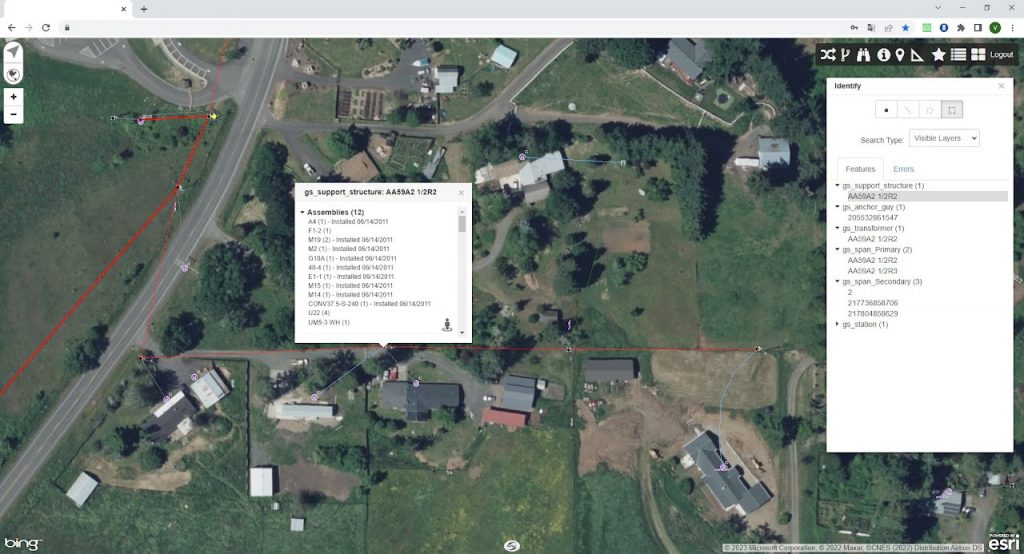
Can be an utility company GIS map, which contains pole data, information concerning framing, quipment, conductor types, etc.
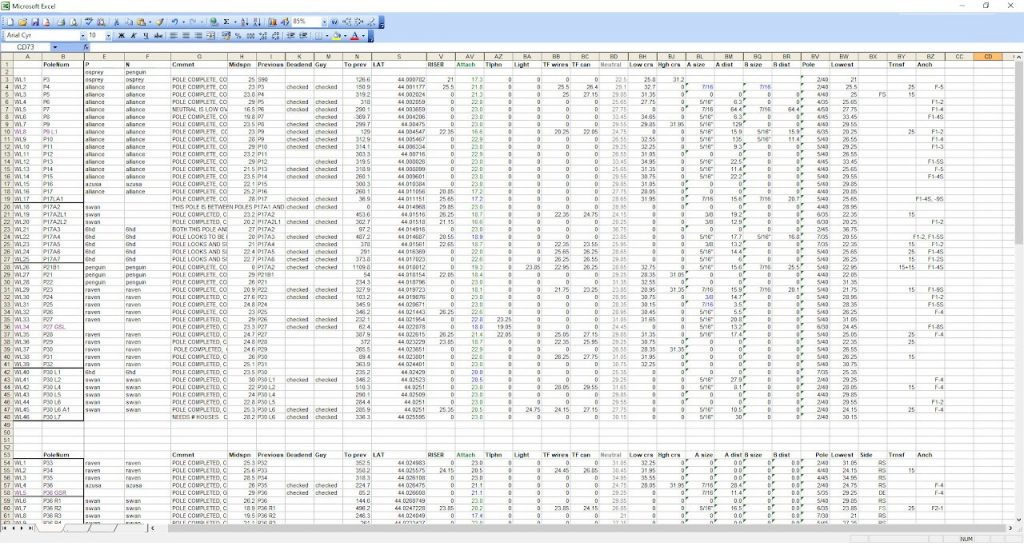
All pole data can be collected in an excel or any other similar file type.

A handwritten survey will also work.
Pole field survey file example: XLS
Considerations in pole loading analysis
- Material – wood, steel, concrete, or composite poles behave differently under stress. It is important to either define the wood type of a pole or obtain this data from local PUC, because even close materials like ordinary fir and douglas fir have different strength.
- Environmental factors – carefully pick wind speed zones, ice loads, seismic activity, soil parameters. Soil type defines the holding strength of poles and anchors.
- Safety margins – align with applicable standards like NESC or ANSI. Double check everything.
- Line tension – watch out for starting and resulting tension and sag, double check that starting tension is above minimum and the resulting tension is below maximum. Unfortunately Ocalc doesn’t support wire galloping calculations.
- Aging and deterioration – is a serious factor in degradation over time for older poles as it reduces the poles overall allowed loading. Be sure to manually add dents, cracks and other stuff if it has been spotted during survey.
- Geometry – always check that isolators are correctly oriented, a straight line of wire is really straight, as even a 1-2 degree kink of wire line can add serious loading to the pole.
What you get
What you get is a complete package of stuff to get permission to attach from your utility company, including:
- Line design file containing all poles in line (PPLLD)
- Separate pole design files for every pole (PPLX)
- Analysis reports (PDF)
- Pole map / Plan view drawing
- Spreadsheet with pole data, including name, type, coords, make ready requirements, pole loading %, etc.
Alongside with help sending it to your utility company, negotiating and defending the solutions.
Is O-calc the best software for pole loading analysis?
Amongst similar software like poleforeman and spidacalc, O-Calc Pro is considered as most powerful and fast, producing the most comprehensive analysis reports.
- It’s specifically designed for utilities and supports NESC compliance.
- Offers advanced 3D modeling capabilities for various equipment and load scenarios.
- Supports integration with GIS systems and field data collection.
- Supports automatic rendering from field photos.
- Provides detailed reports and visualization of stresses and loading conditions.
Alternatives to O-Calc include:
- PLS-CADD/PLS-POLE: Popular for transmission and distribution line analysis, though pretty expensive.
- Spidacalc, Katapult, Poleforeman: Another specialized software for pole loading and infrastructure modeling.
- Sag10: Focused on conductor sag and tension, often used in conjunction with pole analysis tools.
FAQ
How much does it cost?
Pole loading analysis starts from $50/pole and depends on provided data completeness, complexity of work, amount, etc.
How long does it take?
Up to 1 month per 100 poles
Where can I attach?
Communication cables are usually allowed to be attached in communication zone 18′ – 23′.
Communication cables must have 40′ separation from supply conductors per Rule 235 Table 235-5 NESC 2017.
What ground clearances should be maintained?
Check NESC 2017 cheat sheet for clearances.
How to determine framing?
Check US DoA RUS BULLETIN 1728F-804 for specifications for 12.47/7.2 kV line construction
What is the max span of my fiber cable?
A very rough estimation (in meters) can be made as Lmax = (T+1)*10, where T is the tensile strengh of your cable (in kN). To get the accurate numbers follow the standard rules of cable state calculation.
Need to perform PLA? Shoot us a letter, we’ll help.