The results of the development of small-sized optical cables with round steel wire armor are presented. Their design and manufacturing technology ensure high mechanical parameters -allowable working load under elongation, transverse strength, and good flexibility.
- maximum possible mechanical strength with minimum (less than 0.5%) relative elongation;
- minimum weight and dimensions;
- high manufacturability;
- minimum cost.
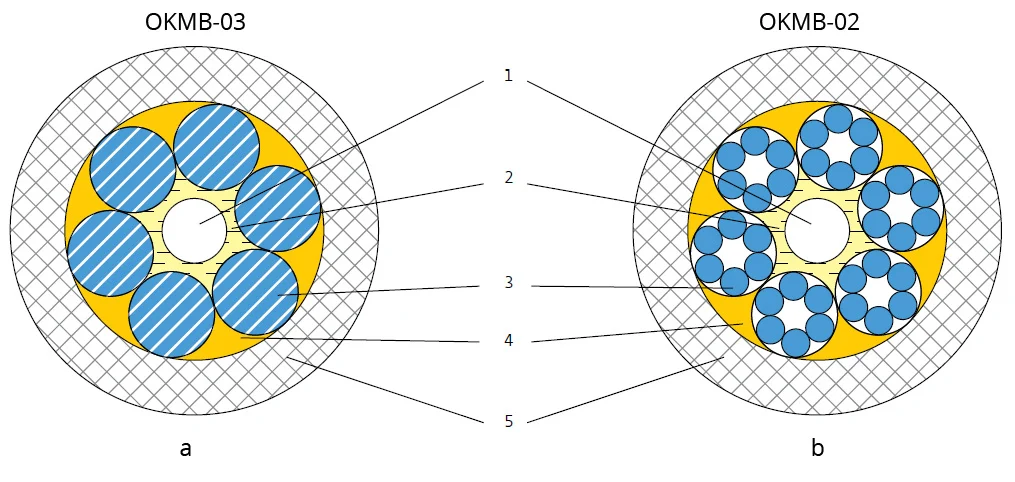
Pic. 1 OKMB-03 and OKMB-02 cable designs
1 – quartz fiber optic cables in a varnish coating (SM or MM)
2 – hydrophobic filler
3 – armor coating made of galvanized steel wires or wire strands
4 – outer hydrophobic filler
5 – hose
In the OKMB-03 design (pic. 1a), the optical fibers are located freely directly inside an armored tube made of steel rope wires.
In the second design, OKMB-02 (pic. 1b), the optical fibers are freely located directly inside an armored tube made of steel wire strands.
During the manufacturing process, a ready-made seven-wire or seven-strand rope with a diameter of 2.4 mm is used. This initial rope, up to 8 km long, is installed as a feeder on the production line, then six wires of the outer layer of this rope are twisted and the armor is formed directly over the four optical fibers (the fibers are inside the rope). The result is a flexible steel «tube – metal module» with a hole, inside which the fibers are located, and the free space is filled with a hydrophobic compound.
The described technological process is carried out in one stage at an average speed of 5 to 25 meters per minte, depending on the diameter of the module (or cable).
The hose material is UV-resistant polyethylene or a polymer that does not support combustion and does not emit halogen-containing toxic substances. FOCs do not contain tubular polymer optical modules, which increases their fire resistance.
The second of the designs mentioned, OKMB-2, is more flexible.
- diameter of the armor coating – from 1.0 to 4.0 mm;
- number of fibers – up to 16;
- maximum allowable tensile load – up to 9 kN;
- allowable transverse pressure – 5 kN/10 cm;
- operating temperature range – -60..+70 °C;
- outer diameter – up to 7.0 mm.
| Cable type | Fiber count | Breaking strength, kN | Cable weight, kg | Armor diameter, mm | Cable diameter, mm |
| OKMB-03 | 1 | 0.6 – 1.0 | 8.5 – 15 | 1.2 – 1.6 | 1.8 – 2.6 |
| OKMB-03 | 2 | 2.0 | 25 | 2.0 | 3.2 |
| OKMB-03 | 4 | 2.5 | 32 | 2.4 | 3.6 |
| OKMB-03 | 8 | 3.5 – 4.5 | 40 – 45 | 2.8 – 3.1 | 4.2 – 4.7 |
| OKMB-03 | 12 | 5.0 – 6.0 | 60 – 72 | 3.3 – 3.7 | 4.9 – 5.1 |
| OKMB-03 | 16 | 6.0 – 7.0 | 72 – 85 | 3.7 – 4.0 | 4.7 – 5.5 |
| OKMB-01 | 1 | 0.5 | 15 | 1.5 | 2.6 |
| OKMB-02 | 2 | 1.0 | 20 | 2.0 | 3.2 |
| OKMB-02 | 4 | 2.0 | 28 | 2.4 | 3.6 |
| OKMB-02 | 8 | 2.5 | 35 | 2.9 | 4.1 |
| OKMB-02 | 12 | 3.0 | 50 | 3.3 | 4.7 |
| OKMB-02 | 16 | 4.0 | 60 | 3.7 | 5.5 |
In the third basic design of optical cable – OKPB (pic. 2) – the optical fibers are located inside a polymer tube. The armor consisting of 12 or 18 steel wires is twisted over the tube. The difference in design is that the armor layer is not made by twisting, but using the technology discussed earlier. As in OKMB cables, the armour braid is not made from individual wires, but is twisted directly from ready-made metal ropes, and has either 12 or 18 wire braids made from preformed steel wires with a diameter of 0.6 to 1.0 mm. The diameter of the cable is from 3.0 to 5.0 mm with an allowable tensile load of up to 10 kN.
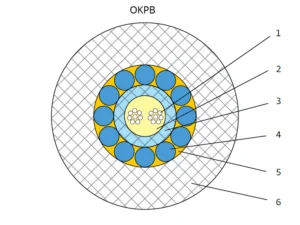
Pic. 2 Cables with a central polymer module
1 – quartz fiber optic cables in a varnish coating (SM or MM)
2 – intra-module hydrophobic filler
3 – polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) module
4 – armor coating made of galvanized steel wires
5 – outer hydrophobic filler
6 – hose
- diameter of the first armor coating – from 3.0 to 5.2 mm;
- fibers used – MM and SM with lacquer coating according to G.652, G.657 specs;
- number of optical fibers – from 1 to 32;
- allowable tensile load:
- from 2.5 to 10 kN – for single-layer armor;
- from 12 to 20.0 kN – for double-layer armor;
- allowable transverse crushing force – from 3 to 10 kN/10 cm for single-layer armor;
- operating temperature range – -60..+70 °C;
- outer diameter – from 3.0 to 9.0 mm (for FOC with single-layer armor).
| Cable type | Fiber count | Breaking strength, kN | Cable weight, kg/km | Module diameter, mm | Armor diameter, mm | Cable diameter, mm |
| OKPB / 2.5 kN | 6 | 2.5 | 40 | 1.8 | 3.0 | 4.2 |
| OKPB / 3.0 kN | 8 | 3.0 | 45 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 4.5 |
| OKPB / 3.5 kN | 8 | 3.5 | 52 | 2.1 | 3.6 | 5.6 |
| OKPB / 5.0 kN | 12 | 5.0 | 75 | 2.4 | 4.0 | 6.6 |
| OKPB / 7.0 kN | 16 | 7.0 | 92 | 2.75 | 4.6 | 7.0 |
| OKPB / 8.0 kN | 24 | 8.0 | 115 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 8.0 |
| OKPB / 10.0 kN | 32 | 10.0 | 140 | 3.4 | 5.2 | 9.0 |
Conclusion
OKPB cables with single-layer armor can be used in urban communication networks. OKP2B cables with double-layer armor can be used for critical installations, including harsh soil conditions. The developed designs create a basis for a significant reduction in the range of cable products and allow for comprehensive and cost-effective solutions to the tasks at hand.
Take care of your splice sheets
1000+ ISPs are already saving weeks of work with Splice.me!